Understanding the Differences Between AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning

Despite this ubiquity, confusion persists about the distinctions between Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL). Understanding these differences isn’t just academic – it’s crucial for businesses investing millions in digital transformation and professionals navigating the evolving tech landscape.
This comprehensive guide demystifies these interconnected yet distinct technologies, helping you make informed decisions about which approach best suits your needs.
What Is Artificial Intelligence and How Does It Work?
Artificial Intelligence represents any computer system designed to mimic human cognitive functions like reasoning, learning, and problem-solving. AI encompasses the overarching field that includes both machine learning and deep learning as specialized subsets.
Think of AI in technology as the umbrella term – it includes everything from simple rule-based chatbots to complex neural networks powering autonomous vehicles. Traditional AI systems operate through programmed rules and logic trees, making decisions based on predefined parameters without necessarily learning from experience.
Key Characteristics of AI:
- Problem-solving capabilities
- Natural language processing
- Computer vision
- Reasoning and planning
- Knowledge representation
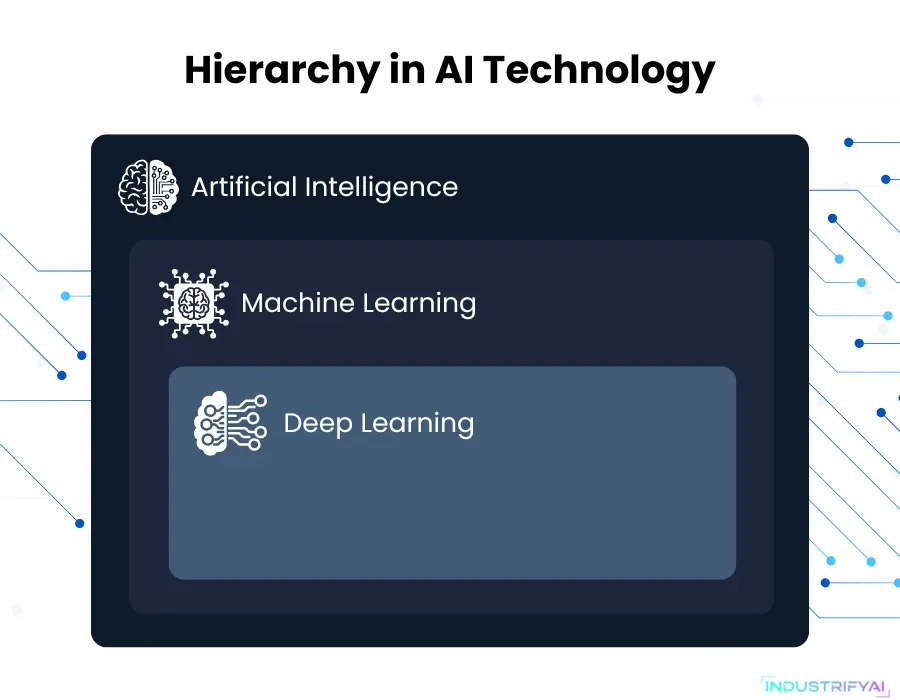
What Makes Machine Learning Different from Traditional AI?
Machine Learning revolutionizes traditional AI by enabling systems to learn and improve from experience without explicit programming for every scenario. Unlike conventional AI that follows predetermined rules, ML algorithms identify patterns in data and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
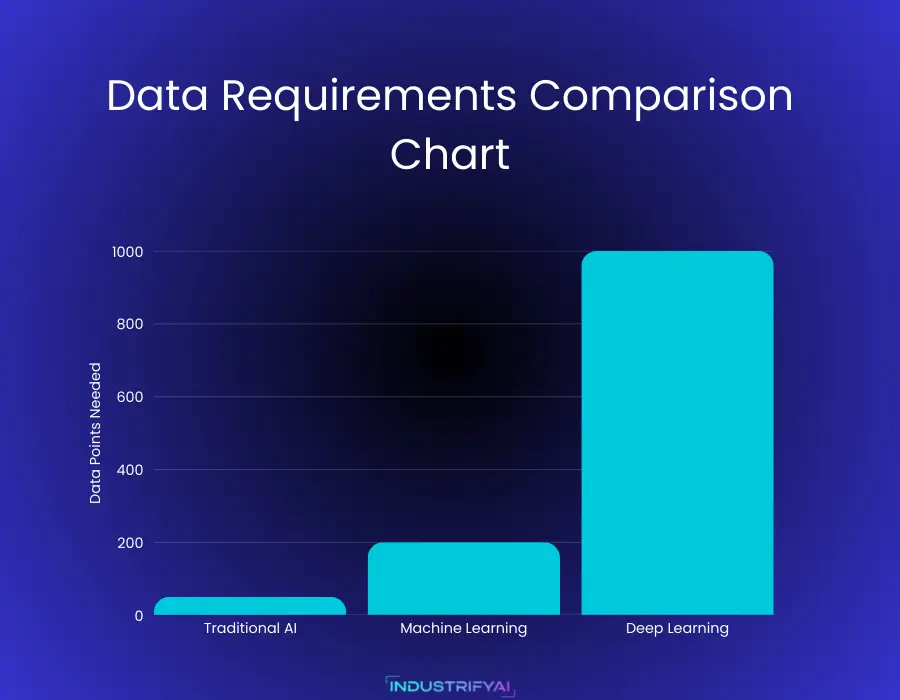
An ML model typically requires about 50-100 data points per feature to function effectively, making it accessible for businesses with moderate data resources. This self-learning capability transforms how AI in technology solves complex problems – from email spam filtering to credit card fraud detection.
Machine Learning Process:
Data Collection → 2. Training → 3. Model Creation → 4. Prediction
The beauty of ML lies in its adaptability. When Gmail filters spam with 99.9% accuracy or when Amazon recommends products you’re likely to buy, that’s machine learning in action.
How Does Deep Learning Advance Beyond Machine Learning?
Deep Learning represents the cutting edge of AI in technology, using artificial neural networks inspired by the human brain’s structure. While ML needs 50-100 data points per feature, deep learning models require thousands of data points per feature to achieve optimal performance.
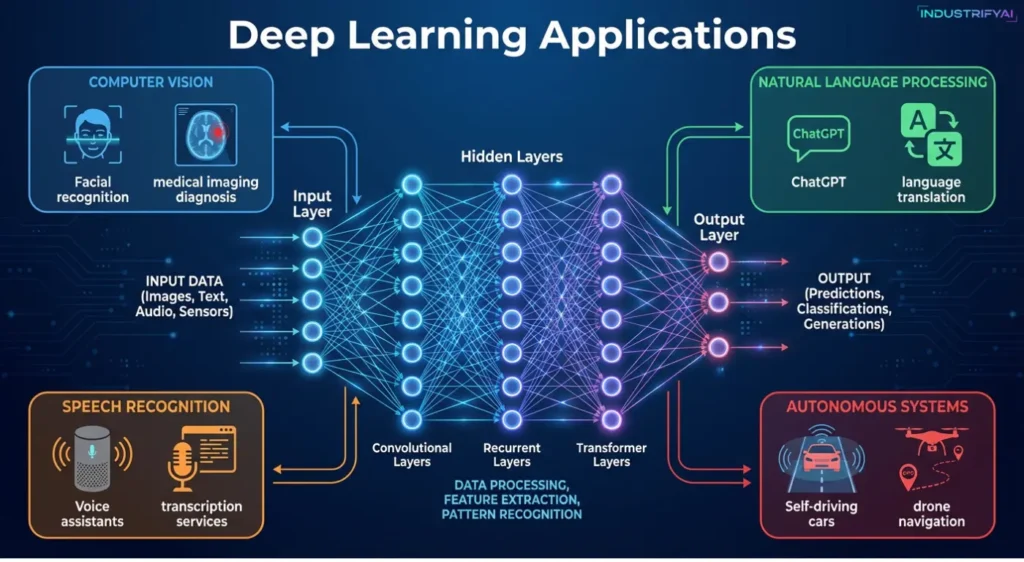
The “deep” in deep learning refers to multiple hidden layers in neural networks – sometimes exceeding 100 layers – that progressively extract higher-level features from raw input. This automatic feature extraction eliminates the need for manual feature engineering, a time-consuming process in traditional ML.
Deep Learning Applications:
- Computer Vision: Facial recognition, medical imaging diagnosis
- Natural Language Processing: ChatGPT, language translation
- Speech Recognition: Voice assistants, transcription services
- Autonomous Systems: Self-driving cars, drone navigation
What Are the Key Differences Between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
Understanding the distinctions helps organizations choose the right technology for their specific needs. Here’s a comprehensive comparison:
Technical Specifications Comparison
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broadest concept | Subset of AI | Subset of ML |
| Data Requirements | Varies widely | 50-100 points/feature | 1000s points/feature |
| Human Intervention | High (rule-based) | Moderate (feature selection) | Minimal (automatic) |
| Computing Power | Low to High | Moderate | High (GPU required) |
| Training Time | Minutes to hours | Hours to days | Days to weeks |
| Interpretability | High (rule-based) | Moderate | Low (black box) |
| Implementation Cost | $ – $$$ | $$ | $$$ |
Performance & Capability Matrix
| Criterion | Traditional AI | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Good for simple tasks | Better with more data | Best for complex patterns |
| Scalability | Limited | Good | Excellent |
| Feature Engineering | Manual | Semi-automatic | Automatic |
| Problem Complexity | Simple to moderate | Moderate to complex | Highly complex |
| Real-time Processing | Fast | Moderate | Slower (but improving) |
Which Industries Benefit Most from AI in Technology?
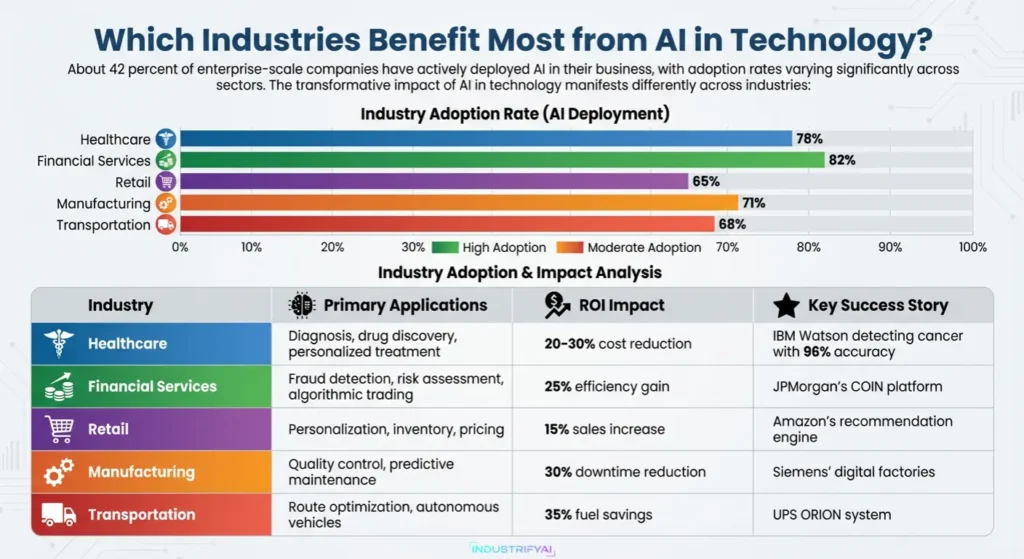
About 42 percent of enterprise-scale companies have actively deployed AI in their business, with adoption rates varying significantly across sectors. The transformative impact of AI in technology manifests differently across industries:
Industry Adoption & Impact Analysis
| Industry | Adoption Rate | Primary Applications | ROI Impact | Key Success Story |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | 78% | Diagnosis, drug discovery, personalized treatment | 20-30% cost reduction | IBM Watson detecting cancer with 96% accuracy |
| Financial Services | 82% | Fraud detection, risk assessment, algorithmic trading | 25% efficiency gain | JPMorgan’s COIN platform |
| Retail | 65% | Personalization, inventory, pricing | 15% sales increase | Amazon’s recommendation engine |
| Manufacturing | 71% | Quality control, predictive maintenance | 30% downtime reduction | Siemens’ digital factories |
| Transportation | 68% | Route optimization, autonomous vehicles | 35% fuel savings | UPS ORION system |
What Are the Real-World Applications You Encounter Daily?
AI in technology has seamlessly integrated into our daily routines, often operating invisibly in the background. Here are applications you likely use without realizing their technological sophistication:
Morning Routine:
- Smartphone Face Unlock (Deep Learning): Neural networks analyze 30,000+ facial data points
- Weather Apps (Machine Learning): Predictive models analyzing historical patterns
- Email Filtering (Machine Learning): Gmail blocks 99.9% of spam using ML algorithms
Throughout the Day:
- Navigation Systems (AI + ML): Google Maps processes real-time traffic from millions of users
- Social Media Feeds (Deep Learning): Instagram’s algorithm analyzes engagement patterns
- Virtual Assistants (All three): Siri uses AI for queries, ML for preferences, DL for voice recognition
Entertainment & Shopping:
- Netflix Recommendations (Machine Learning): Analyzes viewing patterns of 230+ million subscribers
- Spotify Discover Weekly (Deep Learning): Processes 4+ billion playlists for personalization
- Amazon Shopping (All three): Product recommendations, pricing, inventory management
How Do You Choose Between AI, ML, or DL for Your Project?
Selecting the right technology depends on multiple factors. Here’s a practical decision framework:
Technology Selection Guide
| Choose This | When You Have | Best Use Cases | Avoid When |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional AI | Clear rulesLimited dataNeed explainability | Expert systemsRule-based chatbotsDecision trees | Complex patterns exist |
| Machine Learning | Moderate data (1000s records)Defined featuresClear objectives | Sales forecastingCustomer segmentationFraud detection | Unstructured data dominates |
| Deep Learning | Massive data (millions)Complex patternsGPU resources | Image recognitionNatural languageAutonomous systems | Limited data or computing power |
Decision Flowchart Questions:
- Do you have more than 100,000 data points?
- No → Consider Traditional AI or basic ML
- Yes → Continue to question 2
- Is your data primarily unstructured (images, text, audio)?
- No → Machine Learning likely sufficient
- Yes → Deep Learning recommended
- Do you need to explain every decision?
- Yes → Traditional AI or interpretable ML
- No → Deep Learning viable
- Can you afford GPU infrastructure and longer training times?
- No → Stick with ML or cloud-based DL services
- Yes → Deep Learning optimal
What Does the Future Hold for AI in Technology?
The trajectory of AI in technology points toward unprecedented growth and transformation. The market for AI technologies is expected to grow to over 800 billion U.S. dollars by 2030, driven by breakthrough innovations and expanding applications.
Emerging Trends for 2025-2030:
1. Generative AI Evolution
- Multimodal models combining text, image, and video generation
- Industry-specific AI models with specialized training
- Real-time content creation and adaptation
2. Edge AI Proliferation
- AI processing on devices rather than cloud
- Reduced latency for critical applications
- Enhanced privacy and data security
3. Quantum-AI Convergence
- Quantum computing accelerating ML training
- Solving previously intractable problems
- Drug discovery breakthroughs
4. Autonomous Systems Expansion
- Level 5 autonomous vehicles by 2030
- Fully automated warehouses and factories
- Drone delivery networks
Market Projections by Segment (2025-2030)
| Technology Segment | 2025 Value | 2030 Projection | CAGR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generative AI | $67B | $356B | 39.8% |
| Computer Vision | $45B | $175B | 31.2% |
| NLP | $38B | $142B | 30.1% |
| Robotic Process Automation | $29B | $98B | 27.6% |
How Can Businesses Start Implementing These Technologies?
Successfully integrating AI in technology requires strategic planning and realistic expectations. 65% of companies planning to adopt machine learning say the technology helps businesses in decision-making, but success depends on proper implementation.
Implementation Roadmap:
Phase 1: Assessment (Weeks 1-4)
- Identify specific business problems to solve
- Audit existing data quality and quantity
- Evaluate current technical infrastructure
- Calculate potential ROI
Phase 2: Pilot Project (Months 2-3)
- Start with a low-risk, high-impact use case
- Choose appropriate technology (AI vs ML vs DL)
- Establish success metrics
- Build or partner for expertise
Phase 3: Scale & Optimize (Months 4-12)
- Expand successful pilots
- Integrate with existing systems
- Train staff and establish governance
- Continuously monitor and improve
Resource Requirements Checklist:
| Resource Type | Traditional AI | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Team Size | 1-3 developers | 3-5 including data scientists | 5-10 with DL specialists |
| Data Scientists | Optional | 1-2 required | 2-4 required |
| Infrastructure | Standard servers | Cloud or on-premise | GPU clusters/Cloud |
| Timeline | 1-3 months | 3-6 months | 6-12 months |
| Budget Range | $10K-$50K | $50K-$200K | $200K-$1M+ |
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
Starting too big – Begin with pilot projects, not enterprise-wide transformations
Ignoring data quality – “Garbage in, garbage out” applies especially to ML/DL
Underestimating talent needs – Skilled AI professionals are scarce and expensive
Expecting immediate ROI – AI projects often take 12-18 months to show returns
Neglecting ethical considerations – Bias, privacy, and transparency matter
Why Does Understanding These Differences Matter for Your Success?
As AI in technology continues evolving at breakneck speed, distinguishing between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning becomes crucial for strategic decision-making. Whether you’re a business leader evaluating technology investments, a developer choosing the right tools, or a professional planning your career trajectory, these distinctions directly impact your success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can a system use all three technologies simultaneously?
A: Yes! Modern applications often combine all three. For example, autonomous vehicles use traditional AI for route planning, ML for traffic prediction, and DL for image recognition.
Q: Which technology should startups prioritize?
A: Start with traditional AI or basic ML to prove concepts quickly and cost-effectively. Scale to DL only when data volume and complexity demand it.
Q: How long does it take to see ROI from AI investments?
A: Typically 12-18 months for ML projects and 18-24 months for DL initiatives, though quick wins can emerge within 3-6 months with focused pilots.
Q, Is machine learning better than AI?”
A: Machine learning isn’t “better” than AI-it’s a subset. Instead, think of AI as the umbrella term. ML excels at pattern recognition. However, traditional AI handles rule-based tasks efficiently.
Reference:
- McKinsey Global Institute: “The State of AI in 2024”
- Gartner: “Top Strategic Technology Trends for 2025”
- IDC: “Worldwide AI Market Forecast 2025-2030”
- Deloitte: “Enterprise AI Adoption Survey 2024”


